1. धातुओं का धन विद्युति लक्षण : इस श्रेणी में कोई धातु अपने नीचे स्थित धातु की अपेक्षा धनायन बनाने की अधिक प्रवृति रखती है। अतः इसमें ऊपर से नीचे की और चलने पर धातुओं की धनायन बनाने की प्रवृति क्रमश: घटती है , जिस धातु का मानक अपचयन विभव E जितना अधिक ऋणात्मक होता है। वह धातु उतनी ही अधिक धन विद्युति होती है। धन विद्युति लक्षण के आधार पर धातुओं को तीन वर्गों में बांटा जाता है -
(a.) प्रबल धन विद्युति धातुएँ : क्षार धातुएँ (Li , Na ,K) तथा क्षारीय मृदा धातुएँ (Mg ,Ca) प्रबल धन विद्युति धातुएँ है। इनके मानक अपचयन विभव 2.0 वोल्ट या इससे कम है। क्षार धातुएँ ,मृदा धातुएँ से अधिक धन विद्युति होती है।
(b.) साधारण धन विद्युति धातुएँ : ऐलुमिनियम (Al), ज़िंक (Zn), आयरन (Fe), निकिल (Ni) तथा अन्य धातुएँ जिनका स्थान वैद्युत रासायनिक श्रेणी में हाइड्रोजन और मेंगनीशियम के मध्य होता है, साधारण धन विद्युति धातुएँ कहलाती है।
(c.) क्षीण धन विद्युति धातुएँ : कॉपर (Cu), मर्करी (Hg), सिल्वर (Ag) तथा अन्य धातुएँ जो श्रेणी में हाइड्रोजन के ऊपर स्थित होती है ,क्षीण धन विद्युति धातुएँ कहलाती है। इनके मानक अपचयन विभव धनात्मक होते है।
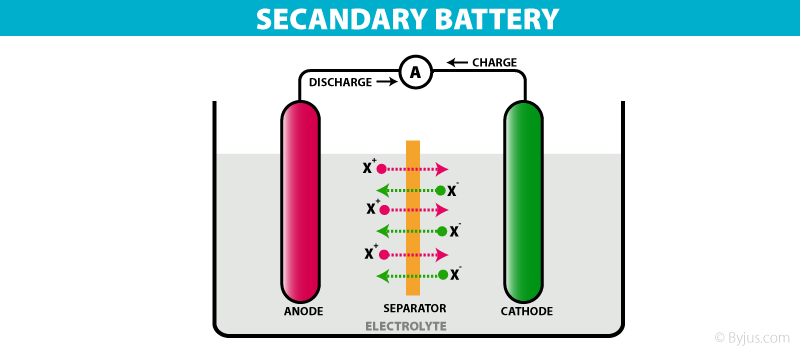
➤2. धातुओं की रासायनिक क्रियाशीलता की तुलना : धातुओं की क्रियाशीलता इलेक्ट्रान त्यागकर धनायन बनाने की प्रवृति पर निर्भर करती है। धातुओं के मानक इलेक्ट्रोड विभव जलीय विलयन में धातुओं की इलेक्ट्रान त्याग करके धनायन बनाने की प्रवृति क्रियाशीलता को परिमाणत्मक रूप व्यक्त करते है।
English Translation :
➤Applications of electrical chemical category: The main applications of this category are as follows.
1. Money electrical characteristics of metals: A metal in this category has a greater tendency to make cation than the metal below it. Therefore, the tendency of metal cation to progress from top to bottom decreases gradually, the more negative the metal the lower the standard reduction potential E. The higher the metal, the richer the power. The metals are divided into three classes based on the characteristic of wealth.
(a.) Strong Wealth Metals: Alkali metals (Li, Na, K) and Alkaline Soil Metals (Mg, Ca) are strong Wealth Metals. Their standard reduction potential is 2.0 volts or less. Alkali metals have more power than soil metals.
(b.) Ordinary Wealth Metals: Aluminum (Al), Zinc (Zn), Iron (Fe), Nickil (Ni) and other metals in the electrochemical category between hydrogen and manganese are called simple metals. is.
(c.) Alkaline Wealth Electrolytic metals: Copper (Cu), Mercury (Hg), Silver (Ag) and other metals which lie above hydrogen in the range are called dilute amines. Their standard reduction potentials are positive.
➤2. Comparison of chemical reactivity of metals: The reactivity of metals depends on the tendency to give up electrons and make cation. Standard electrode potentials of metals quantitatively express the tendency of cation to form by releasing electrons of metals in aqueous solutions.